Is Industry 4.0 Right for Your Business?
Understanding and evaluating Industry 4.0 technologies, tracking the extent to which competitors are implementing smart technologies, and determining what is right for your business are all challenging and critical tasks for medical device company executives. Translating that understanding into a multi-year technology investment and implementation plan further complicates the effort. To provide a starting point, this article summarizes trends, benefits, and challenges of Industry 4.0, sometimes referred to as the fourth industrial revolution.
What Is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 is the digitization of manufacturing using advanced technology including the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), sensors, robotics, complex cloud infrastructure, and next-generation software systems. At the core of Industry 4.0 are the collection and use of enterprise data from which insights are extracted to improve operational practices.
 Benefits of Industry 4.0
Benefits of Industry 4.0
The potential benefits of Industry 4.0 technologies are significant—lower costs, improved quality, greater efficiency, and potentially increased revenues. The following table provides examples of how these benefits are realized through specific applications of Industry 4.0 technologies.
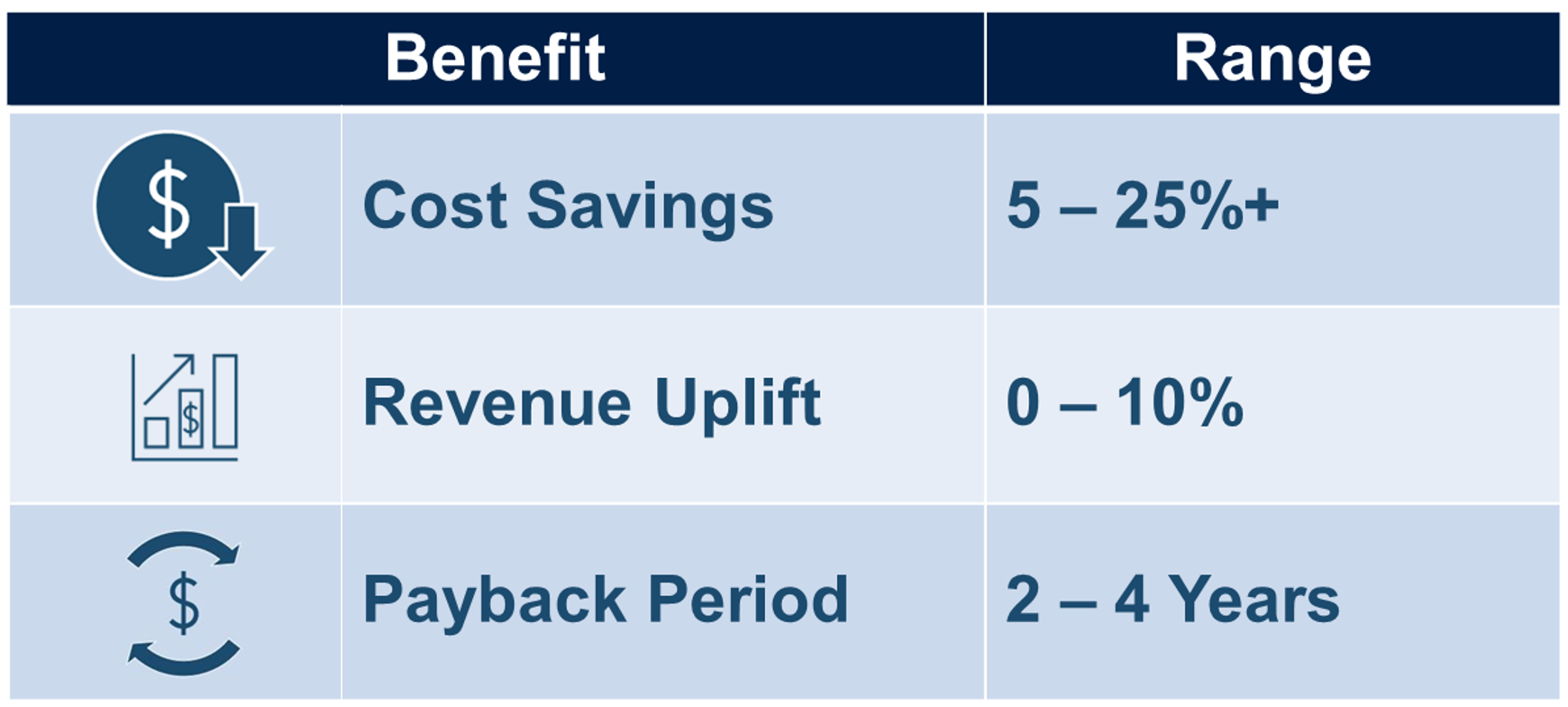
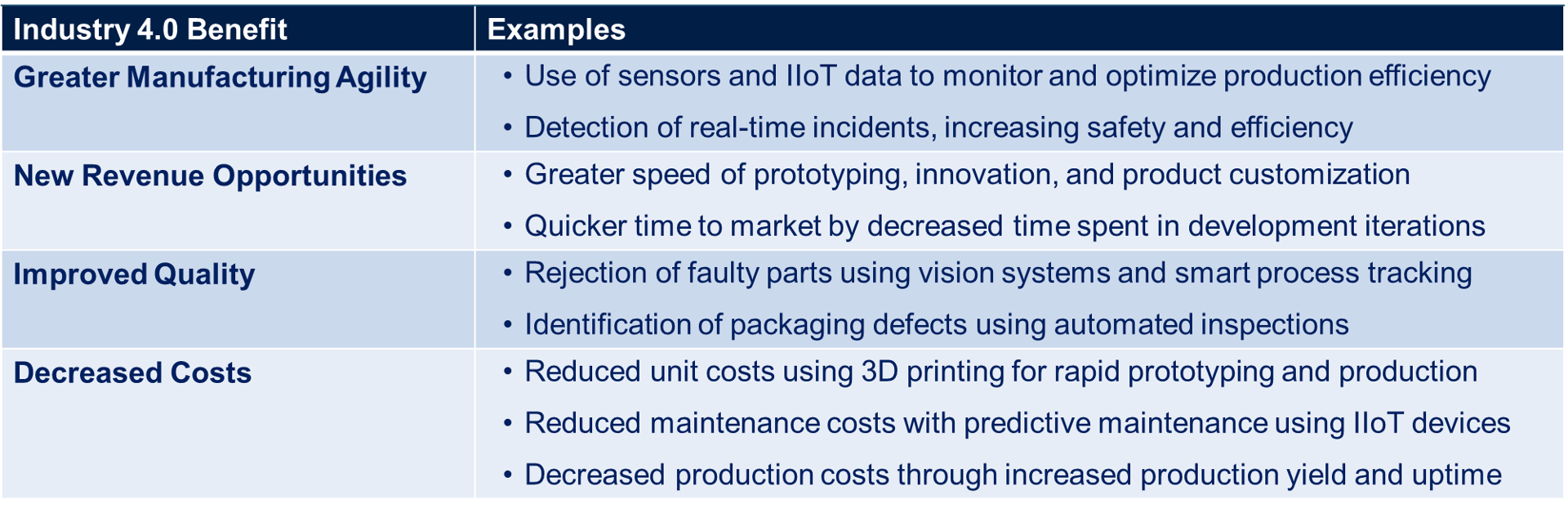 The magnitude of these benefits varies depending on a company’s baseline performance, the extent of Industry 4.0 implementation, and the nature of the business. Companies with a heavy manufacturing focus typically generate the greatest benefits. The following table provides benefit ranges for manufacturing companies.
The magnitude of these benefits varies depending on a company’s baseline performance, the extent of Industry 4.0 implementation, and the nature of the business. Companies with a heavy manufacturing focus typically generate the greatest benefits. The following table provides benefit ranges for manufacturing companies.
 The industries that are adopting Industry 4.0 most readily include Industrial Manufacturing, Aerospace and Defense, Automotive and Transportation, Energy and Utilities, Consumer Goods, and Life Sciences.
The industries that are adopting Industry 4.0 most readily include Industrial Manufacturing, Aerospace and Defense, Automotive and Transportation, Energy and Utilities, Consumer Goods, and Life Sciences.
Challenges to Implementing Industry 4.0 Technologies
While many organizations are implementing Industry 4.0 technologies, the worldwide uptake is not without its challenges. The magnitude of capital investment, managing cybersecurity, and change management represent some of the challenges faced by companies implementing these technologies.
Capital Investment
Industry 4.0 technologies can be adopted in varying degrees. Depending on the complexity of the implementation, the price tag can vary from a small, one-time capital purchase to a deep, long-term capital investment. On the simple side, execution can be as minimal as installing a cobot or IIoT sensors on an assembly line. While the costs of these simpler instances are lower, so, too, are the expected benefits.
On the more complex side, Industry 4.0 implementations can be as complicated as building a fully automated lights out factory that runs around the clock. For extensive Industry 4.0 implementations, the cost to acquire and integrate the machinery, infrastructure, and technology can be significant. While these expenditures may seem large at first, the potential benefits of reducing costs, bringing products to market faster and with higher quality, and having more manufacturing agility may be enough to offset and justify the investment.
Cybersecurity
With more data floating through cyberspace, there are more opportunities for that data to be either unintentionally breached or fall into the wrong hands. Complex, digitally connected IIoT networks enable data to flow from individual machines to central hubs, the cloud, and other smart manufacturing locations. The cybersecurity challenge is to protect intellectual property and competitively sensitive operational data. As Industry 4.0 machinery and devices are implemented, it is equally important to ensure that your cybersecurity protocols, systems, and capabilities are robust enough to ensure the security of sensitive data.
Change Management
Industry 4.0 often involves the coexistence of advanced technology, both hardware and software, with human workers. The incorporation of advanced systems means that the way things are done will change—both on the manufacturing floor and in the office. The acceptance of advanced and novel technologies will require a learning curve from employees who might be unfamiliar. Some employees may feel intimidated or threatened by new technologies, but the intent of Industry 4.0 is to make daily operations more efficient, allowing all employees to achieve greater productivity by focusing on higher-level tasks rather than standard, repetitive procedures that can be handled by a smart robot or software program. Identifying opportunities for employees to provide greater value in conjunction with smart technology is important for championing change towards the use of Industry 4.0 technologies.
In the fast-changing world of manufacturing, keeping pace with competitors requires ongoing evaluation of new technologies to enhance productivity and efficiency. Industry 4.0 and the technologies that it encompasses are the next opportunity for significant gains.









